Pile Sonic Logging Test (SLT)
SONIC LOGGING TEST

Sonic Logging Test
The Sonic Logging Technique, also known as the Cross Hole Ultrasonic Method (CHUM), is used to detect defects in cast-in-situ piles, caissons, barrettes, and diaphragm walls. This method offers a cost-effective way to assess each pile, complementing more expensive capacity testing typically performed on only a small percentage of piles.
Importance of Pile Homogeneity
Ensuring the homogeneity of foundation piles is crucial for their serviceability and load-bearing capacity. Common issues in bored pile construction include:
- Honeycombing: Caused by inadequate vibration
- Segregation: Resulting from over-vibration or improper concrete placement
- Cement Washout
- Cracks in the Pile Shaft
- Inclusions and Necking: Occur when sidewalls collapse during temporary liner withdrawal
Addressing these potential defects during installation is essential to ensure the structural integrity of each pile.
Why Use the Sonic Logging Test?
The Sonic Logging Test effectively detects defects mentioned above. In homogeneous concrete with consistent quality, the velocity of sonic wave propagation remains constant. This technique identifies acoustic irregularities between access tubes within the pile:
- Defect Detection:
A sudden increase in travel time at a specific depth suggests a defect or localized low-quality concrete.
The Cross Hole Ultrasonic Method is recognized in several standards, such as AFNOR (1993) and ASTM (2002). Advanced implementations of this method can provide high-quality results, making it a reliable tool for comprehensive pile assessment.

Testing Procedures
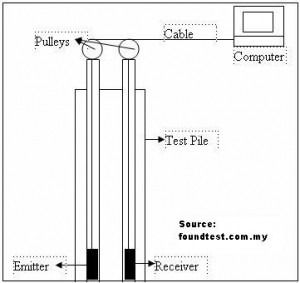
The sonic method is classified as an external test method because it only accesses the top of the pile. The procedure involves lowering two probes into separate access tubes within the pile. One probe acts as an ultrasonic emitter, while the other functions as a receiver.
Once the probes reach the bottom, they are simultaneously pulled upwards to generate an ultrasonic logging profile. The transmitter emits continuous ultrasonic waves in all directions, some of which eventually reach the receiver.
Data Collection and Interpretation:
The testing instrument records and plots the travel time of the ultrasonic waves between the probes against the pile depth.
- Constant Travel Time: Indicates consistent concrete quality throughout the pile.
- Sudden Increase in Travel Time: Suggests a defect or irregularity at that depth, indicating issues such as voids or low-quality concrete.
This cross-hole method is recognized in established standards, including AFNOR (1993) and ASTM (2002), ensuring its reliability and accuracy for pile integrity assessment.
For more information, quotation or site appointment, please call us or drop us a message here.
